Augmented Reality: Definition and Examples (2024)
If you have ever used a tool like Street View or an application to see how your house would look furnished, then you have experienced an augmented reality (AR) experience.
There have surely been many other examples you've encountered, even if you haven't realized it, such as the filters you use on Instagram Stories
.jpg)
If you have ever used a tool like Street View or an application to see how your house would look furnished, then you have experienced an augmented reality (AR) experience.
There have surely been many other examples you've encountered, even if you haven't realized it, such as the filters you use on Instagram Stories.
These are also examples of augmented reality! It's something that is increasingly becoming a part of our lives. That's why in today's article we will explore:
- What augmented reality is
- The role of data in this technology
- Its basic characteristics
- Some additional examples
So let's find out what it's all about and the role that data plays in it.
What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented reality (AR) is a virtual representation of the real world through "computer-generated digital information" and various technologies, such as machine learning.
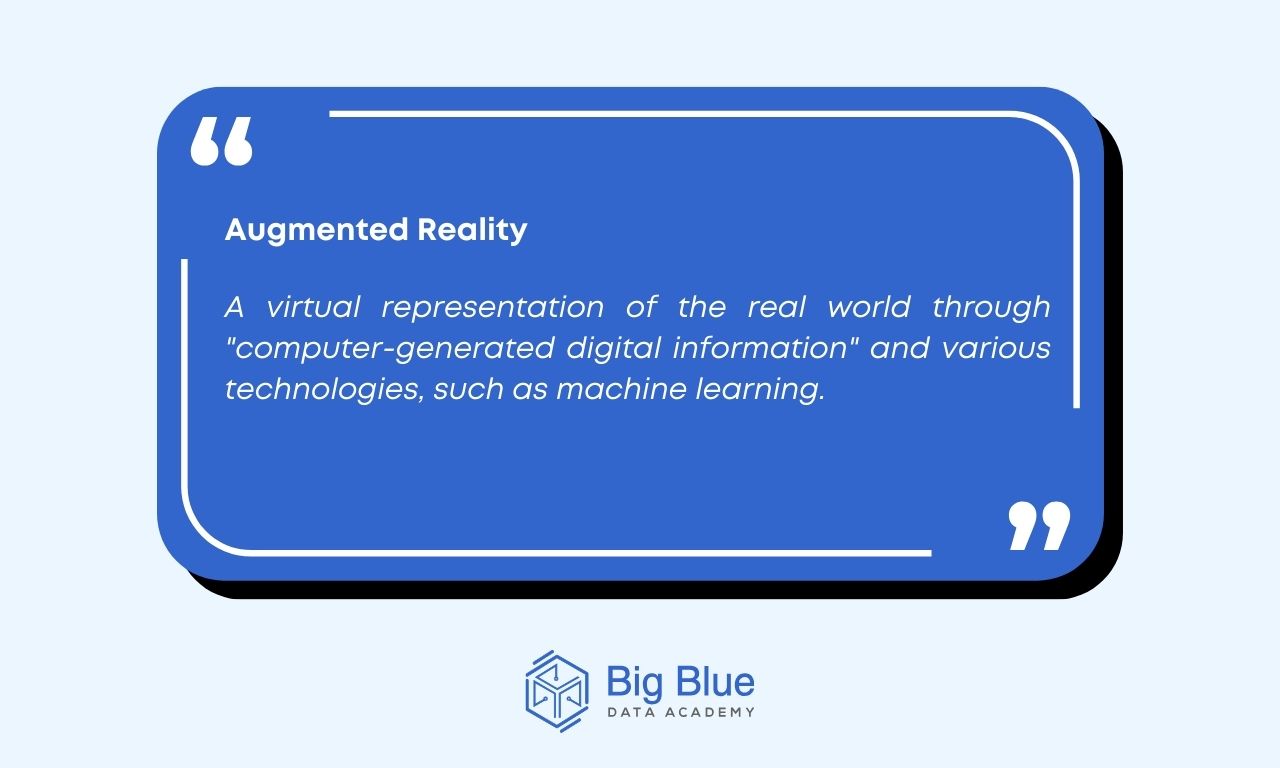
These pieces of information can include elements related to our senses, such as visual and auditory elements. Therefore, AR uses software and hardware to combine digital information with the real world to create a specific result.
Note: Augmented reality (AR) should not be confused with virtual reality (VR). The former uses the environment of the real world, while the latter is entirely in a virtual environment.
We'll see more specific examples later on, but it's worth mentioning the importance of data in this technology and how it continuously improves.
The Role of Data in Augmented Reality
Since a key part of augmented reality is primarily to detect points from the environment of the real world (faces, streets, rooms, etc.), it is essential to collect and then analyze data to better understand what it's about.
This processing of data is done either on the device itself or on remote servers and is something necessary. This is because it involves various tasks, such as:
- Object and image recognition
- Sensor fusion
- Spatial mapping
Sensor fusion, in particular, is crucial as it combines data from various sensors to create a more comprehensive understanding of the user's environment.
Now let's take a closer look at the basic characteristics that make up augmented reality.
Basic Characteristics of Augmented Reality
Primarily, there are three things on which augmented reality is based:
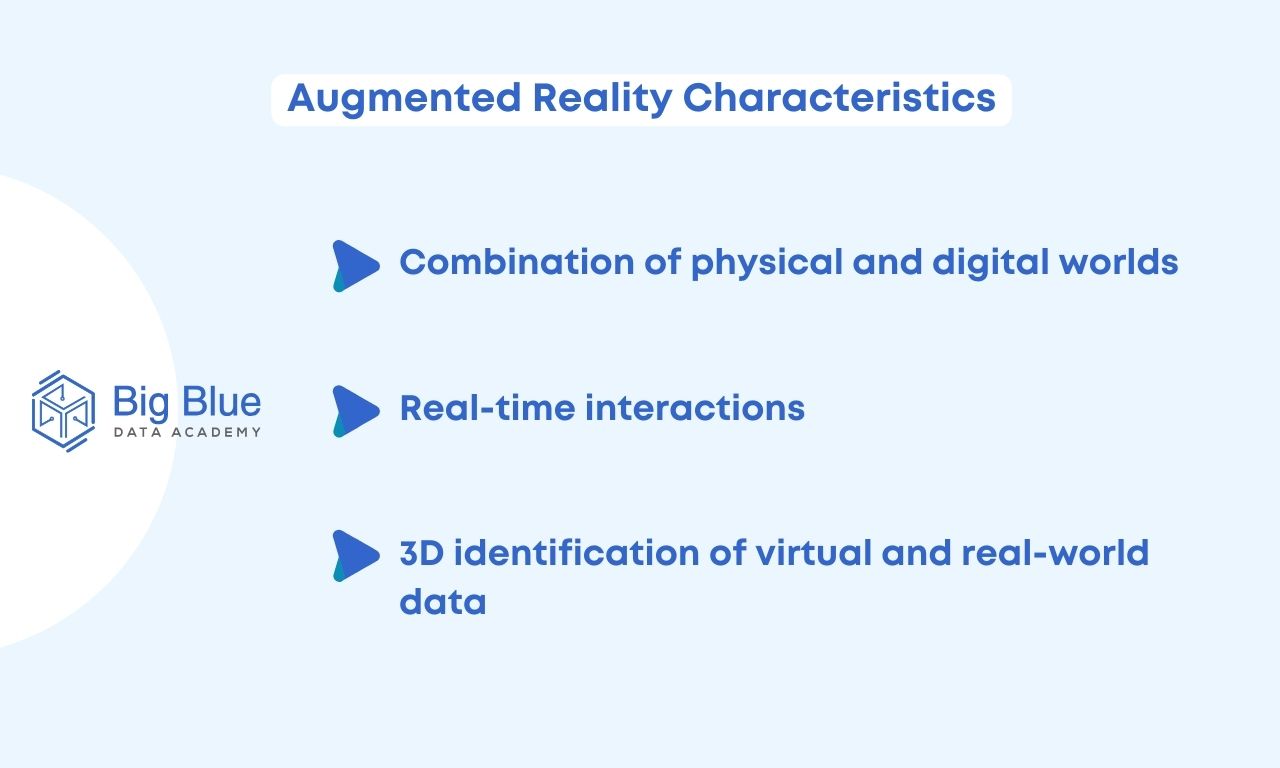
Combination of physical and digital worlds
AR overlays digital information onto the real environment, creating a composite environment where virtual objects coexist with physical ones.
This blending allows users to experience an enhanced version of reality, where digital content complements and interacts with the physical environment.
Real-time interactions
AR applications facilitate real-time interactions between users and virtual elements.
Whether it's manipulating virtual objects, receiving dynamic updates, or participating in digital experiences, AR systems' responsiveness enhances user engagement and interaction.
3D identification of virtual and real-world data
AR technology can accurately map the environment and seamlessly integrate virtual objects into the physical space. This includes precise recognition and positioning of both virtual and real elements within the environment, ensuring smooth interaction and alignment between the two worlds.
Now that we've summarized what augmented reality is, its role of data in it, and its characteristics, let's delve into a few more examples to make it more understandable.
3 Real-Life Examples of Augmented Reality
Below, we'll not just see a few AR examples but real examples from companies that have used this technology for a specific purpose.
Example #1: IKEA
How many times have you thought of buying furniture without being sure if it would fit or match your home?
IKEA attempted to solve this problem by applying augmented reality to help users see exactly how a piece of furniture would look in a room.
Through IKEA Place, users can "try out" any furniture digitally on their mobile devices to ensure their purchase before actually buying it.
This resulted in the app being downloaded by more than half a million users by 2020!
Example #2: Coca Cola
Another major company, Coca-Cola, used AR to enhance the experience of stores that are its customers.
Specifically, retailers can see how a Coca-Cola fridge would look in their store through their mobile or tablet, obviously without it actually being there!
-copy-3.jpg)
Example #3: Amazon
A giant like Amazon couldn't be missing from the list of companies that have leveraged the power of AR. Similarly to IKEA, Amazon wanted to help its users "see" how they look wearing specific clothes, such as shoes.
This not only helped the company offer a better and more enhanced experience for its customers but also further established it as a company at the forefront of new technologies and innovation.
These are benefits that any company adopting a technology like AR can have.
To Sum Up
So far it's clear that augmented reality is a technology that is here to stay.
And this is because it offers multiple advantages, both for the user and for those who create and offer it.
But how is such a technology constructed?
Certainly, it's not simple, as it requires various skills, from machine learning to programming, such as knowledge of Python. So if you’d like to enrich your knowledge, read more related articles on our blog!

-copy-4.jpg)
.jpg)