Data Ingestion: Definition, Types & Process (2024)
Many times, the data we collect does not require immediate processing or application, so it is stored for future use.
This is the essence of Data Ingestion, which we will discuss today, specifically:
- What is Data Ingestion
- Its basic types
- The process it follows
As well as the various advantages it offers.
What is Data Ingestion?
As mentioned, Data Ingestion (or in simpler terms, "data absorption" or "data intake") refers to the collection of data and often their processing for future use, once they have been stored in a database.
However, no matter where this data comes from, such as:
- Social media
- Databases
- Web scraping
Or anywhere else, the purpose is for the data to be used immediately when the time comes, for their intended purpose.
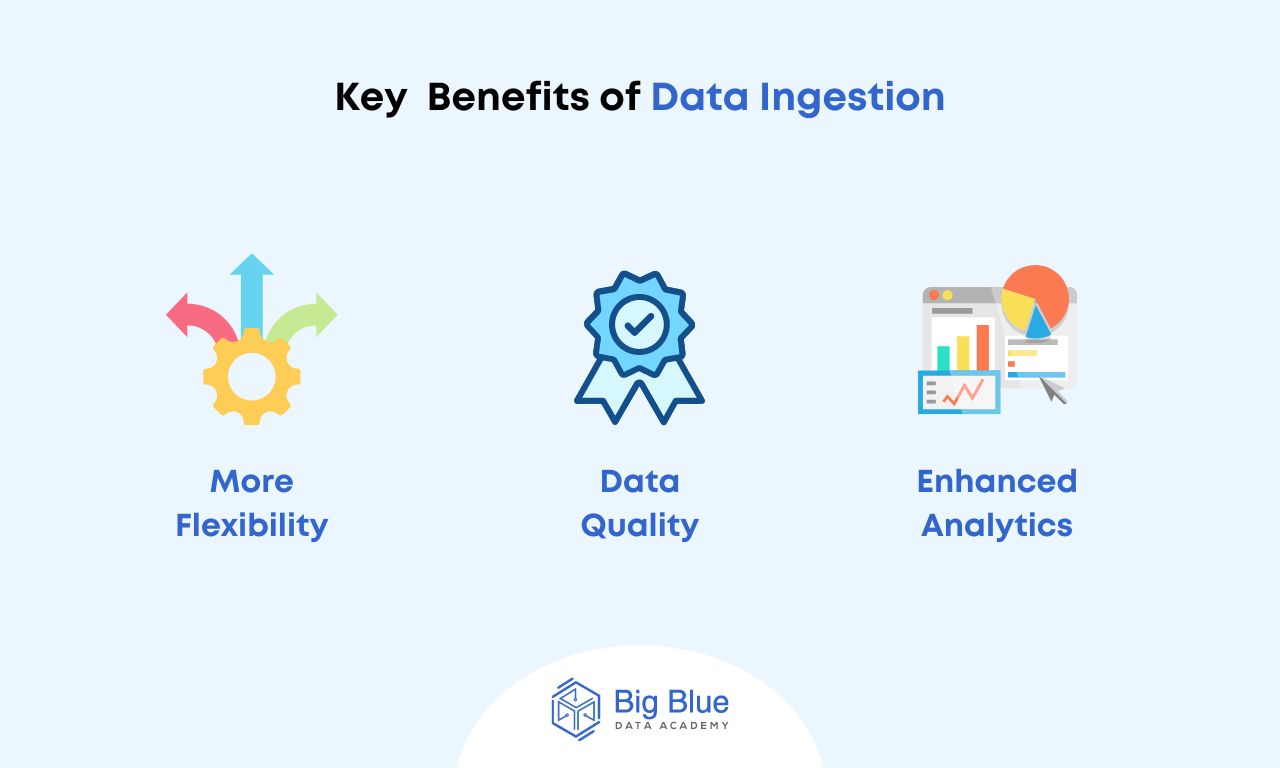
The reasons why Data Ingestion is important vary, with the most basic ones being:
- The flexibility it offers, as data sources can be multiple and their structure different. Therefore, the ability to process and "ingest" this data for a period of time provides a better picture to a business.
- The quality of the data, which can be enhanced as further changes, improvements, analyses, and data cleaning can be done during Data Ingestion.
- Improved analytics, as without an effective data ingestion process, it would be impossible to gather and prepare the vast amounts of data required for more detailed analyses.
Now that we've covered some basics, let's delve deeper into Data Ingestion by analyzing its basic types.
3 Basic Types of Data Ingestion
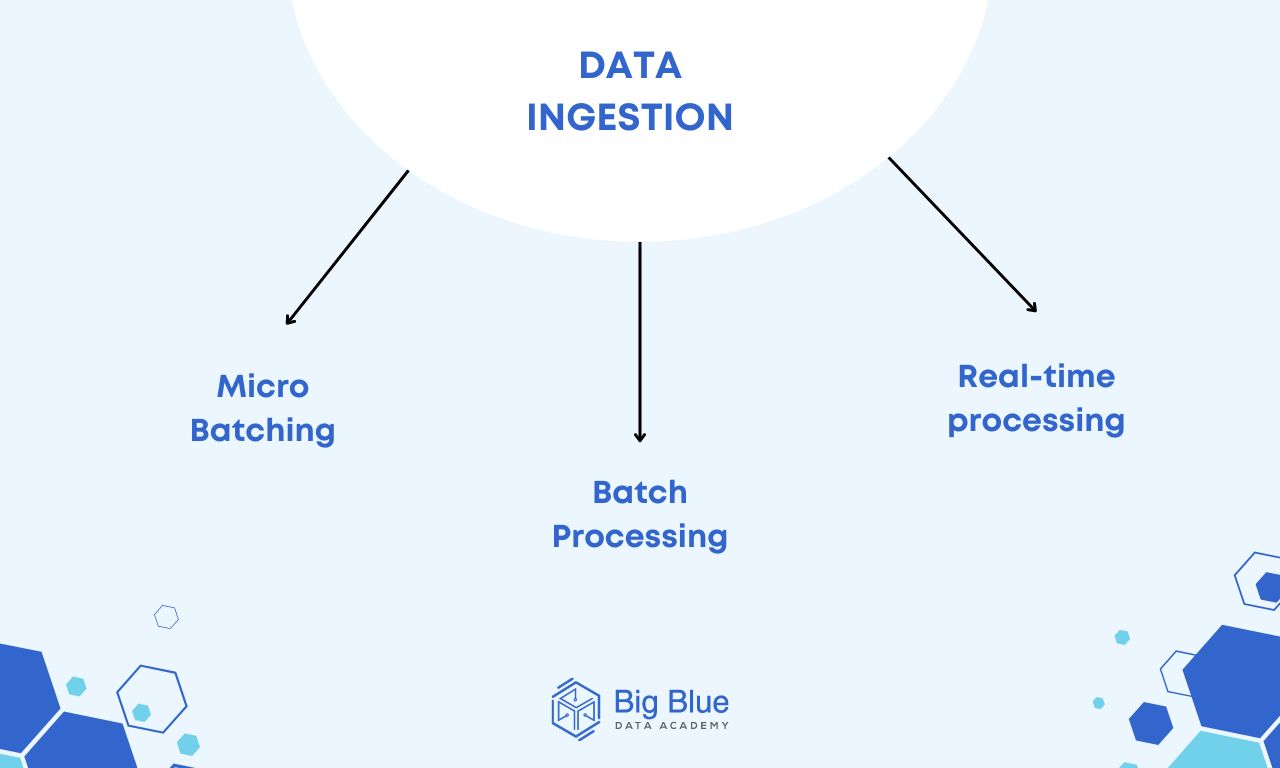
Micro-batching
Micro-batching is a hybrid model that combines the two types we'll see below.
Essentially, it involves introducing data in small "batches," allowing frequent real-time updates without the resource demands of real-time processing.
Batch Processing
Batch processing is a type of data ingestion where data is collected over a specific period of time and then processed all together.
This method is useful for tasks that do not need to be updated in real-time and can be executed during off-peak hours (such as overnight) to minimize the impact on system performance.
Real-time Processing
Real-time processing involves the immediate ingestion of data as soon as it is generated. This allows for immediate analysis, making it ideal for time-sensitive applications.
While real-time processing can provide immediate insights and faster decision-making, it requires significant computational power and a more advanced data infrastructure to handle this continuous data flow.
Specifically, what is the process followed by data ingestion?
Let's see.
The Process Data Ingestion Follows
The process follows 5 basic stages and can be summarized as follows:
Data Discovery: Involves exploring and understanding the available data, identifying data sources, understanding their structure, and determining how they can be used to benefit the organization.
Data Acquisition: The next step is data acquisition, which involves gathering data from various sources and integrating them into the organization's system.
Data Validation: Once the data is acquired, it undergoes extensive validation to ensure its accuracy and consistency.
Data Transformation: After validation, the data undergoes transformation to convert it from its original form to a format suitable for analysis and processing. This transformation process may include techniques such as normalization, merging, and standardization.
Data Loading: The final step in the data ingestion process involves loading the transformed data into a designated location, such as a data warehouse, for further analysis or reporting.
In a nutshell
So, we've seen what Data Ingestion is, what it involves, and its benefits. Undoubtedly, it is a complex but important process for anyone involved in it, regardless of their position in a data team.
So if you're involved in this subject and want to enrich your knowledge, read more related articles on our blog!


.jpg)